The Mediterranean Diet Food Pyramid is a visual tool used to describe the foods on the Mediterranean diet, highlighting the ones we should aim to increase and reduce for well-being and longevity.
Whether you’re new to the Mediterranean diet or looking for sustainable healthy eating guidance, the pyramid can be a great tool for you.
What Is The Mediterranean Diet?
The Mediterranean Diet is a nutritious eating pattern and lifestyle. It comes from the Mediterranean region, where over 20 countries border the Mediterranean Sea. The region is filled with diverse landscapes which provide an abundance of fresh produce that inspired this way of eating and living.
The Mediterranean diet became popular through research conducted by Ancel Keys and Antonia Trichopoulou beginning in the 1960s that showed an association between the diets in these regions and low rates of cardiovascular disease. Since then, thousands of studies on the Mediterranean diet have consistently highlighted its numerous health benefits.
What Is A Food Pyramid?
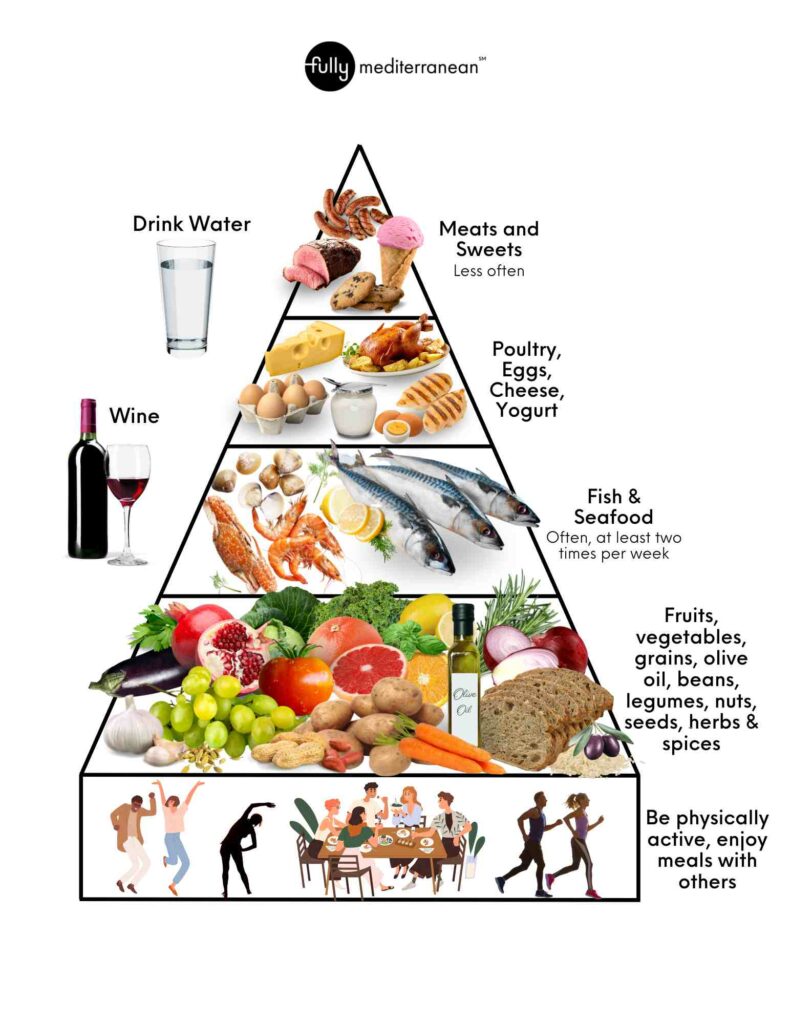
A food pyramid is a diagram with several sections within a large triangle that describes the relative amounts of different foods in a diet. The bottom of the pyramid is the largest section indicating that these types of foods are regularly consumed on the diet and encouraged.
The next sections on the pyramid are slightly smaller and indicate that those food groups should be consumed in smaller quantities and less frequently.
The top of the food pyramid is reserved for foods eaten the least frequently and that we want to limit in our day-to-day lives. This generally includes items that are high in sugar, saturated fat, and sodium.
What Is The Food Pyramid In The Mediterranean Diet?
The Oldways Mediterranean diet food pyramid is a visual representation of the food groups that are encouraged and limited on the Mediterranean diet. The Mediterranean Diet Food Pyramid was developed in 1993 by Oldways, in partnership with the Harvard School of Public Health and the World Health Organization. Oldways is a nonprofit that highlights cultural food traditions.
As you will notice in the pyramid below, the Mediterranean diet is unique because it incorporates healthy lifestyle components such as physical activity and social meals with friends and family. The other sections of the pyramid describe how much of the other food groups are encouraged and limited on the Mediterranean diet relative to one another.
There are no specific quantity recommendations because diet is highly individualized to each person. Instead, the Mediterranean diet gives you a relative comparison of which food groups are consumed in greater quantities and frequencies according to their nutrient profiles.
We recommend printing out the Mediterranean diet food pyramid to have as a reference in your kitchen when building meals.
Download Our Printable Food Pyramid for Free
What Are The Main Foods In A Mediterranean Diet?
Plant-Based Foods
The largest section of the Mediterranean diet food pyramid is filled with nutrient-dense produce, whole grains, legumes, nuts and more. You will notice that this is the largest food category, and it is made up of all vegetarian ingredients. While the Mediterranean diet isn’t exclusively vegetarian, it is a plant-forward diet. These plant-based foods are high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Olive oil is included in this same section because it is a crucial component of the Mediterranean diet. Olive oil is high in healthy unsaturated fats that support cardiovascular health. In the same section, we also see herbs and spices because they are high in antioxidants.
Fish and Seafood
The next section is made up of fish and seafood. Seafood is high in protein and low in saturated fats. Seafood also contains omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins and minerals such as vitamin D, iron and zinc. Fish and seafood are recommended to be consumed at least twice per week on the Mediterranean diet. The Mediterranean Diet encourages eating fatty fish rich in omega 3 fatty acids such as salmon, tuna, and whitefish.
Poultry and Dairy Products
The next section above seafood is smaller and includes lean meat like chicken, and dairy products such as milk, cheese, and eggs. These foods contain protein, calcium, and other minerals, but they also contain some saturated fat.
Meats and Sweets
The topmost section is meats and sweets. These foods are high in saturated fat and sugar. Overconsumption of these foods increases your risk of heart disease and other health problems such as brain health and weight gain.
Beverages
Water and wine are noted on the side of the pyramid. Water should be consumed as the primary drink throughout the day. Hydrating with water is one of the best ways to start incorporating the Mediterranean diet. Wine is consumed in small quantities with occasional meals.
What Is Not Allowed On The Mediterranean Diet?
The Mediterranean diet is a non-restrictive way of eating. This is one of the key reasons why it’s a sustainable diet people can stick to throughout their entire lives. No foods are completely ruled out on the Mediterranean diet. Instead, we focus on which food groups are consumed in relatively lower quantities.
Meat
Meat, particularly red meat, is consumed in smaller quantities. Red meat is high in saturated fat, which is associated with an increased risk of heart disease. Therefore, red meat consumption is reserved for special occasions.
Sugar, Sodium, and Saturated Fat
Foods high in sugar, sodium, and saturated fat are recommended to be consumed less often. This includes fried foods, highly processed foods, and sugary desserts.
The Mediterranean diet is a well-rounded way of living and eating. The meals are flavorful, vibrant, and delicious. It’s a sustainable way of eating for the environment by reducing meat consumption and for its flexibility, with all foods included in moderation.
Looking For More?
One of our most popular resources is our free guide on how to start the Mediterranean diet, which gives you actionable steps to incorporate the diet into your life.


0 Comments